这篇学习下链码,原文在这里,写的很好,这里就不做详细描述了,但会做一些扩展,并会进行下总结。
基础概念
Fabric 的智能合约称为链码(chaincode),分为系统链码和用户链码:
- 系统链码用来实现系统层面的功能,包括系统的配置,用户链码的部署、升级,用户交易的签名和验证策略等。
- 用户链码用于实现用户的应用功能。开发者编写链码应用程序并将其部署到网络上。终端用户通过与网络节点交互的客户端应用程序调用链码。
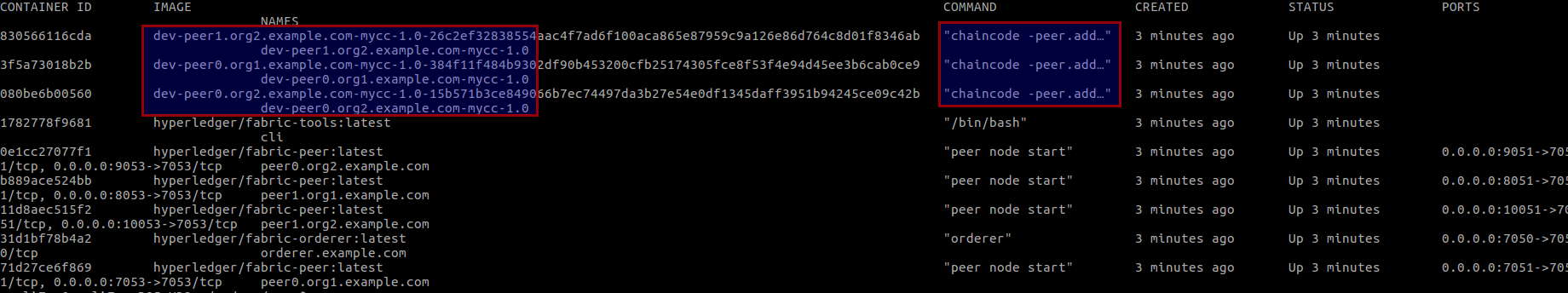
链码被编译成一个独立的应用程序,运行于隔离的Docker容器中,在链码部署的时候会自动生成合约的Docker镜像。看下之前的 byfn 的教程中创建的所有的 container,标记的这几个就是独立的链码容器:
相较于以太坊,Fabric 链码和底层账本是分开的,升级链码时并不需要迁移账本数据到新链码当中,真正实现了逻辑与数据的分离。
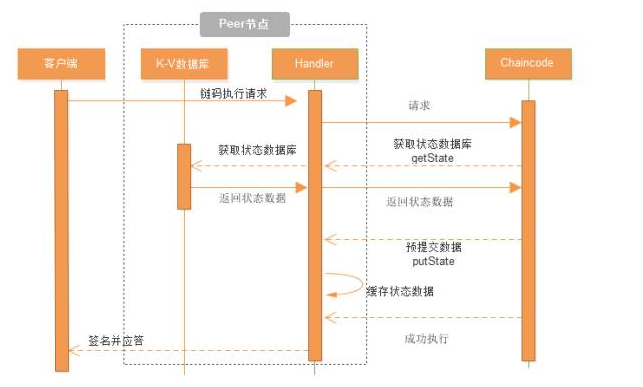
链码可以调用另一个链码,不一定非要在同一个 channel 内。当调用另一个 channel 内的链码的时候,只能使用 query 接口。
有一种链码 API 还能够提供额外的控制,每个资产的 key/value 中可以包含客户的身份识别,这样只允许这个客户才能够更新这个资产。
chaincode lifecycle API
package
package 包含三个部分:
- chaincode,用 CDS (Signed ChaincodeDeploymentSpec) 定义,包含代码、名称、版本等。
- 可选的实例化规则,语法与背书规则类似
- 拥有 chaincode 的组织的签名
- 用来确定 chaincode 的所有权
- 用来验证 package 的内容
- 用来检测 package 贿赂
这个命令主要是用来生成 SignedCDS,用于多签名的情况。
如果只是单签名,直接使用 install 就好。
下面这条命令是,生成 chaincode package,并签名
1 2 3 4 5
# 生成并签第一个名 peer chaincode package -n mycc -p github.com/hyperledger/fabric/examples/chaincode/go/example02/cmd -v 0 -s -S -i "AND('OrgA.admin')" ccpack.out # 其他人签名 peer chaincode signpackage ccpack.out signedccpack.outinstall
这条命令发送 SignedProposal 给 LSCC (lifecycle system chaincode,在 System Chaincode),会创建 SignedCDS,并在节点上安装。
1
peer chaincode install -n asset_mgmt -v 1.0 -p sacc
instantiate
instantiate 会调用 LSCC 在 channel 上创建和初始化 chaincode,chaincode 可能会在多个 channel 上安装和初始化,但是相互之间是独立的。
channel MSP 的管理者可以调用 instantiate 来实例化一个 chaincode,当这个交易请求到达背书节点的时候,需要验证创建者的签名,在节点提交到账本的时候,还需要再验证一遍。
在 instantiate 的时候,可以提供初始值,也需要提供背书规则:
1
peer chaincode instantiate -n sacc -v 1.0 -c '{"Args":["john","0"]}' -P "AND ('Org1.member','Org2.member')"upgrade
upgrade 可以升级 chaincode 代码和版本,但是名字必须保持不变,另外实例化规则使用的是现有的规则,这个保证了升级的合法性。
另一点是,upgrade 是针对单个节点的,这个节点更新了 chaincode,但是其他的节点可能还是使用的旧版本,这个需要注意。
最后一点是,upgrade 会调用合约的 Init 函数,在这里可以进行升级和重初始化数据的工作,因为会操作数据,所以也需要注意不要弄丢数据。
peer chaincode 命令用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
Usage:
peer chaincode [command]
Available Commands:
install Package the specified chaincode into a deployment spec and save it on the peer's path.
instantiate Deploy the specified chaincode to the network.
invoke Invoke the specified chaincode.
list Get the instantiated chaincodes on a channel or installed chaincodes on a peer.
package Package the specified chaincode into a deployment spec.
query Query using the specified chaincode.
signpackage Sign the specified chaincode package
upgrade Upgrade chaincode.
Flags:
--cafile string Path to file containing PEM-encoded trusted certificate(s) for the ordering endpoint
-h, --help help for chaincode
-o, --orderer string Ordering service endpoint
--tls Use TLS when communicating with the orderer endpoint
--transient string Transient map of arguments in JSON encoding
Global Flags:
--logging-level string Default logging level and overrides, see core.yaml for full syntax
--test.coverprofile string Done (default "coverage.cov")
-v, --version
Use "peer chaincode [command] --help" for more information about a command.
几个 chaincode API 和 函数
API:
- Init,在链码 instantiate 或 upgrade 的时候会调用,做一些必要的初始化工作,必须实现。
- Invoke,链码调用的主要入口函数,在这里根据提供的函数名,调用不同的自定义的函数,必须实现。
函数:
1
args := stub.GetStringArgs() # 初始化时,从交易中获取参数
1
err := stub.PutState(args[0], []byte(args[1])) # 写入状态
1
fn, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters() # 从交易中获取函数名和参数
1
value, err := stub.GetState(args[0]) # 读取状态
System chaincode
文章简单介绍了下 system chaincode:
LSCC Lifecycle system chaincode handles lifecycle requests described above.
这个与 chaincode 生命周期相关的,上面介绍那些都是这个范围。
CSCC Configuration system chaincode handles channel configuration on the peer side.
这个与 channel 的配置有关,我们知道虽然 channel 配置是各个 channel 自己定义的,但是系统会管理所有的配置。
QSCC Query system chaincode provides ledger query APIs such as getting blocks and transactions.
这个我想与之前说过的,新加入节点需要从 order 节点获取区块有关。
System Chaincode Plugins
system chaincode 是以插件的形式存在的,在节点启动的时候注册并部署。
编译 system chaincode plugins,用下面的命令,编译的结果是 .so:
1
go build -buildmode=plugin
fabric 的 core.yaml 中也需要进行相关的配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
...
chaincode:
systemPlugins:
- enabled: true
name: mysyscc
path: /opt/lib/syscc.so
invokableExternal: true
invokableCC2CC: true
...
chaincode:
system:
mysyscc: enable
其他注意点
下面这条命令在国内用,很可能长时间没有反应
1
go get -u github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim
可以直接 clone fabric 的源码,然后将源码放入到 go/src/github.com/hyperledger 下
1 2 3
cd ~/go/src/github.com mkdir hyperledger && cd hyperledger git clone git@github.com:hyperledger/fabric.git
创建 chaincode 容器,有两种方式。一种是直接创建 chaincode 的容器,在容器内跑起来 chaincode,然后才在背书节点进行 chaincode 的 install 和 instantiate,另一种是在 byfn 中使用的,在背书节点进行 instantiate 的时候,由系统自动创建一个 chaincode 的容器,而且需要提供 order 节点的证书。
